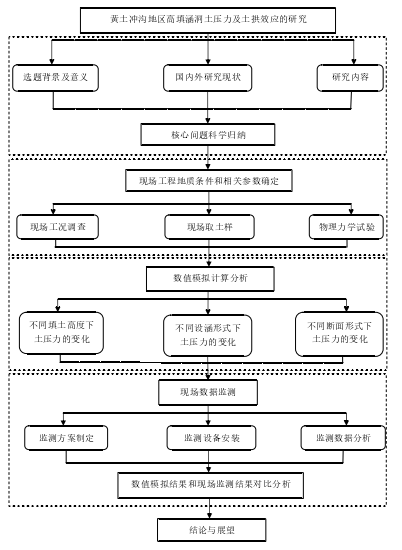
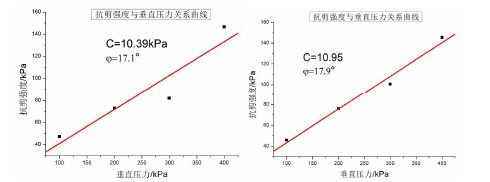
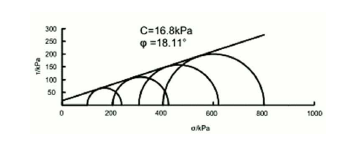
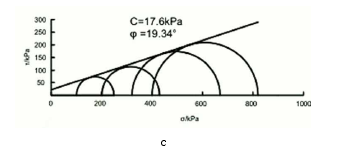
本文通过采用数值模拟分析和现场监测相结合的方法,研究了上埋式和沟埋式两种设涵情况下拱涵、管涵、箱涵三种涵洞在不同填土高度情况下的土压力和沉降变化。首先取样并通过相关试验获得现场岩土参数;然后根据工程实际用CANDE 建立有限元模型,进行计算;最后把所得计算结果和现场监测数据相结合,分析涵洞土压力的变化规律。
(1)在填土高度较低时,三种涵洞上埋式设涵和沟埋式设涵的涵顶垂直土压力差别不大,可近似的用上覆填土的 γH 线性计算,此时无论上埋式还是沟埋式情况下土拱效应都不明显。
(2)对高填情况而言,上埋式设涵时涵洞的涵顶垂直土压力超过了上覆填土 γH 计算值,涵顶产生了土压力集中现象;沟埋式涵洞的涵顶垂直土压力明显小于 γH 计算值,产生了明显的土拱效应,使得涵顶土压力大大减小。产生不同受力情况的原因是上覆土体与两侧土体的沉降差异。上埋式设涵时中心沉降小于两侧土体沉降,两侧土体将荷载传导至涵顶,导致涵顶应力集中;沟埋式设涵时中心沉降大于两侧沉降,两侧土体分担了一部分上覆填土的自重,产生土拱效应,导致涵顶垂直土压力减小。且沟埋式设涵时的中心沉降始终大于上埋式设涵时的中心沉降。
(3)产生土拱效应需要一定的填土高度。对三种涵洞而言,沟埋式设涵时填土高度小于 20m 时,涵顶垂直土压力系数不小于 1,土拱效应不明显;填土高度超过 20m 过后,涵顶垂直土压力系数开始小于 1,涵洞上方的土拱效应变得明显。土拱效应减少的涵顶垂直土压力最高达上覆填土自重的 22%。
(4)对不同类型涵洞而言,拱涵和管涵的受力情况接近,上埋式设涵情况下涵顶垂直土压力系数最大值为 1.19,填土高度无限大时涵顶垂直土压力系数趋向 1,而沟埋式设涵情况下涵顶垂直土压力系数最小值为 0.85 左右;对箱涵而言,上埋式设涵时涵顶垂直土压力系数最大值为 1.33,沟埋式设涵时涵顶垂直土压力系数最小值为 0.78。
(5)沟埋式设涵时沟壁并不绝对垂直的情况下,沟壁与竖直方向所成角度 θ越小,涵顶土压力越小,此时土拱效应越明显,沟壁与竖直方向所成角度 θ 越大,涵顶土压力的值越大。角度 θ 从小到大的过程,实际上就是理想的沟埋式设涵向上埋式设涵过渡的过程。
(6)基于上述结论,提出以下建议:实际工程中,当涵洞的填土高于 22m时,设涵形式首选沟埋式设涵,利用土拱效应减小涵顶的垂直土压力;没有沟埋式设涵施工条件的,可选择上埋式拱涵这一形式,其涵顶垂直土压力系数最大值较小,有利于受力。
本文通过现场监测和数值模拟相结合的手段,对不同设涵情况下的不同涵洞在各填土高度下的土压力分布和土拱效应进行了研究。但在运用有限元软件进行建模时,对一些复杂的实际条件进行了简化处理,这使得本次研究所得的结论具有一定程度上的局限性,存在着一些有待完善的不足之处。
数值模拟中高填方情况下填土高度间距取值为 10m,可以尝试间距取得更小一些,划分得更细一点,以取得更为准确的结果。实际工程中,涵顶垂直土压力系数在允许的条件下,越小则越安全,下一步可以尝试在沟埋式设涵涵洞正上方加一层或多层柔性材料,增大上覆土体的沉降,理论上会使得土拱效应更明显,涵顶垂直土压力系数更小。
另一方面,囿于篇幅和时间,涵洞土压力监测应时间跨度更长,才能确保更全面、准确的反映施工完成后土压力的变化规律。
参考文献
Abbot P. A. Noliner static arching for vertically buried primatic strcture[M].
AFWL-TDR-65-160, Kirkland Airforce Base, aug, 1966.
Abdel Karim , Ahmad M. Structurt response of full-scale concrete box culvert[J].
Journnal of structural Engineering, 1993, 11.
Allgood J. R. Structure in soil under high loads[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Foundations Divisions, ASCE, 1971, 97(3).
American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, Inc. (AASHTO). AASHTO standard specifications for highway bridges[S]. Washington D C: 2002.
American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). Standard specifications for highway bridges, 16th Ed., AASHTO, Washington, D.C.
American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). AASHTO LRFD bridge design specifications, 2nd Ed., AASHTO, Washington, D.C.
Binger, W. V. Discussion to ‘Underground conduits—An appraisal of modernresearch’ . Proc. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng., 73,1543–1545.
Braune, G. M., Cain, et al. Earth pressure experiments on culvert pipe. Public Roads,10(9), 153–176.
Brinkgreve R.B.J,Vermeer P.A. Finite element code for soil and rock analysis[M]. Rotterdam:Balkema,1998.
Clarke N W . The loads imposed on conduits laid embankments or valley fills[J]. instcivil engineers proc london, 1967.
Dasgupta, A., and Sengupta. Large-scale model test on square box culvert backfilledwith sand[J]. Geotech. Eng. Div., Am. Soc. Civ. Eng., 117(1), 156–161.
Duncan, Michael J . Factors of Safety and Reliability in Geotechnical Engineering[J].
Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2000,126(4):307-316.
GB50010-2010.混凝土结构设计规[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社,2010.
Getzler Z., Komovnik A., Mazurik A.. Modle study on arching above buriedstructure[J]. Journal of the Soil and Foundation Division, ASCE, 1968, 94(5).
Girdler H F . Loads on Box Culverts under High Embankments[J]. earth pressure,1974.
Bao H, Zhai Y, Lan H, et al. Distribution characteristics and controlling factors ofvertical joint spacing in sand-mud interbedded strata. Journal of StructuralGeology, 2019, 128: 103886.
Bao H, Zhang G, Lan H, et al. Geometrical heterogeneity of the joint roughnesscoefficient revealed by 3D laser scanning. Engineering Geology, 2019: 105415.
H?eg, K. Stresses against underground structural cylinders[J]. Soil Mech. Found.
Div., 94(4), 833–858.
JTJ022-85,公路砖石及砼桥涵设计规范[S].北京:人民交通出版社,1985.
K. M El-Sawy. Three-dimensional modeling of soil-steel culverts under the effect oftruckloads[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2003, 41(8):747-768.
Kang J, Parker F, Yoo C H. Soil-structure interaction for deeply recess corrugated steel pipes, part Ⅱ: Imperfect trench installation[J]. Engineering Structures, 2008, 30(3):588-594.
Karinski Y S , Dancygier A N , Leviathan I . An analytical model to evalulate the static soil pressure on a buried structure[J]. Engineering Structures, 2003, 25(1):91-101.
Katona M G , Vittes P D . Soil-Structure analysis and evaluation of buried box-culvertdesigns[C]. Computing in Civil Engineering. ASCE, 1982.
Kyungsik Kim , Chai H. Yoo , F.ASCE , et al. Design Loading on Deeply Buried BoxCulverts [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering , 2005 ,131(1): 20-27.
Lusher U., Hoeg K. The benificial action of the surrounding soil on the load-carryingcapacity of burring tubes[M]. Prceedings of the 1964 Syposium on Soil-StructureInternational held at Tucson, Ariz, 1964.
Marston A., Anderson A.O..The theory of loads on pipes in ditch and tests ofcement and clay drain tile and sever pipe[R]. Bulletin No.31 , Ames: IowaEngineering Experiment Station , 1913.
Marston A..The theory of external loads on closed conduits in the light of the latestexperiments[R]. Bulletin No.96, Ames: Iowa Engineering Experiment Station,1930.
Mcaffee R.P,Valsangkar A.J. Field performance centrifuge testing, and numericalmodelling of an induced trench installation[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2008, 45(1):85-101.
Mirza, S. A., Hatzinikolas, M., and MacGregor. Statistical descriptions of strength ofconcrete[J]. Struct. Div. ASCE, 105(6), 1021–1037.
Nowak, A. S. Calibration of LRFD bridge code[J]. Struct. Eng., 121(8), 1245–1251.
Penman, A. D. M., Charles, J. A., Nash, et al. Performance of culvert under Winscardam. 14F, 4T, 13R : PENMAN, AD BUILDING RES. STN. WATFORD, GBGEOTECHNIQUE, V25, N4, 1975, P713–730[J]. international journal of rockmechanics & mining sciences & geomechanics abstracts, 1976, 13(3):31-0.
Richard M. Bennett. Vertical Loads on Concrete Box Culverts under HighEmbankments[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering,2005, 10(6): 643-649.
Schlock , W.J . Loads on pipe in wide ditches[R]. Iowa Engineering ExperimentStation Bulletin , Iowa State College , Iowa , 1932, NO.108.
Smith A. , Bergmann T . The Design, Construction and Monitoring of reinforced earthculverts on an alluvial floodplain[J]. Joernaal Van Die Suid Afrikaanse InstituutVan Siviele Ingenieurswese, 1994.
Spangler M G. A theory on loads on negative projecting conduits[C].Proceedings ofHighway Research Board, 1950: 153-161.
Spangler M G. Field measurements of the settlement ratios of various highwayculverts[R]. Iowa: Iowa Engineering Experiment Station , 1950.
Spangler M G. Underground conduits——An appraisal of modernresearch[C].Proceedi-ngs of American Society of Civil Engineering, 1947: 855-884.
Stone , K. J. L. Hensley , P. J. Taylor , et al. Centrifuge study of rectangular boxculverts[C]. proceedings of the international Conference Centrifugue , 1991 , Jun13-14.
Sun L , Hopkins T , Beckham T . Stress Reduction by Ultra-Lightweight Geofoam forHigh Fill Culvert: Numerical Analysis[J]. 2006.
Trollope, D. H., Speedie, M. G., Lee, I. K. Pressure measurements on Tullaroop damculvert[J]. Proc., 4th Australia–New Zealand Conf. on Soil Mechanics andFoundation Engineering, 81–92.
Vaslestad J. , Johansen, Holm. Load reduction on rigid culverts beneath high fills:
Long-term behavior. Transportation Research Board , 1415, 58–68.
Wood, S. M. Internal forces in a reinforced concrete box culvert. Master’s thesis, TheUniv. of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tenn.
Woodbury, W. H., Bayer, E. J., Botts, A, et al. Corrugated metal culverts for railroadpurposes. Preparing specifications, with assistance of committee on iron andsteel structures. Bull. Am. Railway Eng. Assoc., 27(284), 794–828.
Yang, M. Z. Evaluation of factors affecting earth pressures on buried box culverts.
PhD dissertation, Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tenn.
白伟方, 何超群. 高填土涵洞垂直土压力分布规律研究[J]. 交通运输研究,2012(2):58-60.
岑国平, 刘晓曦, 王旭. 高填路堤涵洞受力及变形特性有限元分析[J]. 路基工程, 000(1):27-29.
曾国熙.土坝下管道竖向土压力的计算[J].浙江大学学报,1960,(1):79-97.
陈保国, 焦俊杰, 宋丁豹. 钢筋混凝土箱涵竖向土压力理论研究——梯形沟谷设涵[J]. 岩土力学(10):178-185.
顾安全.上埋式管道及洞室垂直土压力的研究[J].岩土工程学报,1981,3(1):3-15.
关亮,陈正汉,黄雪峰,等.非饱和填土(黄土)强度特性的三轴试验研究. 建筑科学,2011,(11):55~57.
郝宪武,白青霞.填埋式管道土压力的弹粘塑性有限元分析[J].西北建筑工程学院学报,1994,(3).
河北省交通规划设计院.公路小桥涵手册[S].北京:人民交通出版社,2002.
黄豪, 赵雷鸣, 邹志强, 等. 高填方涵洞分层回填的数值模拟和土压力分析[J].交通信息与安全, 026(1):96-98.
浑铁链. 太中线黄土地区桥涵的设计.山西建筑,2008,(2):321~323.
孔洋,阮怀宁,黄雪峰.黄土丘陵沟壑区压实回填土地基沉降计算方法. 岩土工程学报,2018,(A1):218~223.
李广信.高等土力学[M].北京: 清华大学出版社,2011.
李盛, 马莉, 王起才, 等. 高填黄土明洞卸载结构土压力模型试验和数值模拟分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, v.38;No.294(4):66-72.
李现立.黄土地区高填土涵洞设计的探讨.城市建设理论研究,2015,5(24):2095~2104.
李永刚, 周慧珍. 涵洞变形对涵顶土压力的影响[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2014,45(6):829-832.
梁东文. 涵洞垂直土压力的试验研究[J]. 中国科技信息, 2005(04):105-106.
林韵梅.地压讲座[M].北京:煤炭工业出版社,1981.
刘旭.湿陷性黄土地区的桥涵设计讨.建筑工程技术与设计,2018,(8):2548.
罗智刚, 李永刚, 李力. 涵洞洞顶垂直土压力的分析及计算[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2004(06):101-104.
马强,郑俊杰,张军.山区涵洞受力影响因素的数值模拟分析[J].合肥工业大学学报:自然科学版,2009,32(10):1514-1517.
牛现民. 高填土涵洞的非线性竖向土压力分析[J]. 河南建材, 2008(2):59-60.
裴元新,顾强康,张仁义,等.黄土压缩特性及高填方填土合理含水率控制. 中外公路,2014,(14):56~60.
彭浩,张汉卿.湿陷性黄土地区的桥涵设计.公路交通科技(应用技术版),2011,(7):127~129.
师影,尹燕运.高填土和软土地基中的涵洞设计问题初探. 黑龙江交通科技,2018,(296):117~118.
宋飞. 黄土地区高填路堤下涵洞上土压力的计算分析[J]. 山西交通科技,2007(1):59-62.
孙 均,侯学渊.地下结构[M].北京:科学出版社,1988.
陶云川.高路堤涵洞土压力计算方法研究[J].山西交通科技, 2012(2):44-46.
王鑫.黄土地区高填土涵洞设计的探讨.青海交通科技,2010,(1):63~64.
王旭,岑国平,刘一通,等.上埋式拱涵应变分布特性及有限元分析[J].公路交通科技,2008,25(9): 81-84.
王长运, 李庆东. 对沟埋式涵洞垂直土压力计算探讨[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2005(8):70-72.
王长运, 李永刚. 矩形断面沟埋式涵洞垂直土压力的分析[J]. 太原理工大学学报(01):36-39.
杨锡武, 张永兴, YANGXi-wu, et al. 山区公路高填方涵洞的成拱效应及土压力计算理论研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(21):3887-3887.
杨锡武, 张永兴. 公路高填方涵洞土压力变化规律及计算方法研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2005, 38(9):119-124.
杨锡武. 高填方涵洞土压力变化规律与影响因素的数值模拟研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 24(5):42-47.
姚伟,张忠平,谭冬生,等.黄土地区某填土斜坡场地地质病害分析研究. 铁道工程学报,2014,(4):41~45.
张勃蓬.谈黄土地区高填土冲沟涵的施工.山西建筑,2011,(32):166~167.
赵建斌. 高填方路堤下涵洞垂直土压力研究[D]. 华中科技大学, 2008.
折学森,顾安全.高填土下管道土压力的分析[J].西安公路学院学报,1992,27-33.
折学森.路基涵洞的土压力计算[J].中国公路学报,1992,5(3):72-79.
周兴涛, 陈保国, 简文星, 等. 沟埋涵洞土拱效应及涵顶垂直土压力研究[J].地下空间与工程学报, 2015(04):151-158.
朱才辉, 李宁, 袁继国. 黄土冲沟中高填方土压力量测及分布规律探讨[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(3):000827-836.