摘 要: 断奶是仔猪面临的一个重大的应激事件,极易造成仔猪断奶应激,破坏仔猪肠道屏障功能。有效降低断奶应激导致的仔猪肠道损伤、提高养分的吸收能力对提高养猪生产经济效益具有重要意义。表皮生长因子(EGF)是一种含有53个氨基酸残基的小分子肽,对动物肠道健康具有营养生理作用。本文主要综述了EGF对断奶仔猪肠道功能的影响及其调控断奶仔猪肠道健康的作用机制,以期为EGF在仔猪生产中的应用提供理论支撑。
关键词: 表皮生长因子; 断奶仔猪; 肠道健康; 肠道屏障; 断奶应激;
Abstract: Weaning is one of the major stress event faced by piglets,which can easily cause weaning stress and destroy intestinal barrier function of piglets.To reduce intestinal damage caused by weaning stress,and improve nutrient absorption capacity of piglets has great significance to improve economic benefit of pig production.Epidermal growth factor(EGF) is a small molecular peptide containing 53 amino acid residues,which has nutritive physiological effects on animal intestinal health.In this paper,the effect of EGF on intestinal function of weaned piglets and its mechanism of regulating intestinal health of weaned piglets were reviewed,so as to provide theoretical support for the application of EGF in piglet production.[Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2021,33(1):-]
Keyword: epidermal growth factor; weaned piglets; intestinal health; intestinal barrier; weaned stress;
仔猪早期断奶可最大限度发挥母猪的繁殖性能,提高母猪年产仔数,对提高养猪生产经济效益具有重要意义[1]。但是,早期断奶可能会因为饮食及环境的改变引发仔猪断奶应激反应。肠道是动物响应应激反应的重要器官,当仔猪发生断奶应激时,肠道内环境易受大肠杆菌等病原微生物的侵袭[2],刺激肠黏膜分泌炎性因子,破坏肠道黏膜屏障功能[3,4],导致仔猪采食量下降,日增重降低,免疫力下降,肠道菌群失衡,甚至引起仔猪死亡[5,6],给养猪生产带来较大经济损失。在限抗、禁抗大背景下,通过营养手段改善断奶仔猪肠道健康状况,对提高养猪生产的经济效益具有重要意义。表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)属于促生长因子家族成员,是一种含有53个氨基酸残基、3个二硫键的小分子肽,具有促进肠上皮细胞增殖与分化的功能,可促进幼龄动物肠道发育及营养物质吸收,加速受损肠道修复进程[7,8,9,10]。EGF对热和酸具有较强耐受性,能抵抗胰蛋白酶、糜蛋白酶及胃蛋白酶的消化。仔猪采食EGF后,通过胃后部分EGF被降解,但残留的EGF在仔猪肠道仍能发挥生物活性[11]。EGF的这些特性使其可作为饲料添加剂直接应用于仔猪饲粮中。研究表明,EGF对断奶仔猪肠道发育及受损肠道修复具有良好的促进作用,可有效缓解断奶应激对仔猪生长的抑制作用[12,13,14]。本文综述了EGF对仔猪断奶肠道健康的影响及其调控断奶仔猪肠道健康的作用机制,以期为EGF在仔猪生产中的应用提供理论支撑。
1、 EGF对断奶仔猪肠道发育的影响
养猪就是养肠道,仔猪的健康状况很大程度上取决于肠道健康状况。仔猪胃肠道功能发育尚不完善,断奶后会因饮食及环境的改变引发断奶应激,导致肠道黏膜形态结构改变,影响肠道营养物质吸收,不利于仔猪健康生长[5,6]。EGF是一种有丝分裂原,具有促进细胞增殖与分化的功能,对幼龄动物胃肠道发育具有重要作用[15]。Kang等[16]利用乳酸菌表达猪源EGF并饲喂21日龄断奶仔猪,发现EGF可促进断奶仔猪肠上皮细胞增殖,并提高小肠绒毛高度及小肠长度。Wang等[17,18]研究表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪十二指肠、空肠、回肠发育,提高其绒毛高度,降低隐窝深度,并促进肠上皮细胞DNA、RNA和蛋白质合成。Bedford等[19]研究表明,EGF可促进空肠发育,提高肠道绒毛高度,降低隐窝深度,并促进肠道杯状细胞增殖分化。Wang等[20,21]研究表明,EGF对断奶仔猪肠道发育具有促进作用,可有效提高断奶仔猪小肠绒毛高度,促进肠道上皮细胞增殖,并促进哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamyoin,mTOR)表达及磷酸化,说明EGF可通过激活mTOR信号通路促进断奶仔猪肠道发育。汤小朋[22]利用脂多糖(LPS)构建仔猪肠道损伤模型研究EGF对LPS刺激的仔猪肠道损伤的修复作用,结果表明EGF对LPS导致的肠绒毛结构损伤具有良好的修复作用,可有效提高LPS刺激的仔猪小肠(十二指肠、空肠及回肠)绒毛高度并降低隐窝深度。以上研究表明,EGF对断奶仔猪肠道发育具有良好的促进作用,并对受损肠道具有良好的修复功能。

肠道完整性是仔猪营养物质消化吸收的结构基础,也是断奶仔猪健康生长的前提。EGF在促进肠道发育的前提下可促进胃肠道消化酶的分泌及营养物质转运载体蛋白的表达。如Lee等[23]研究发现,仔猪饲喂含1.5 mg/kg EGF的饲粮可显着增加空肠碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)及乳糖酶的活性。Bedford等[19,24]研究表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪肠道钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白1(sodium/glucose cotransporter 1,SGLT1)的表达及蔗糖酶分泌。Wang等[12]、Xu等[14]利用乳酸菌构建猪源EGF表达模型,并用于仔猪饲粮中,发现EGF可促进肠道消化酶蔗糖酶、氨基肽酶A(aminopeptidase A,APA)、氨基肽酶N(aminopeptide N,APN)、二肽酶活性及营养物质转运载体钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白1(SGLT1)、葡萄糖转运蛋白2(glucose transporter 2,GLUT2)及小肠肽转运载体1(peptide transporter 1,PEPT1)基因表达。Wang等[20]研究表明,EGF可促进肠道葡萄糖转运蛋白2(Slc2a2)及溶质载体家族6(中性氨基酸转运蛋白6)成员19(Slc6a19)基因及SGLT1、PEPT1蛋白表达,并促进营养物质表观消化率。利用Ussingchamber系统在猪小肠上皮细胞(IPEC-J2细胞)中的研究表明EGF可促进细胞对谷氨酰胺的吸收[25]。正常情况下EGF对肠道磷的吸收起抑制作用[8,26,27],但在应激状态下EGF可通过上调钠磷转运载体蛋白Ⅱb型(sodium dependent phosphate cotransporter typeⅡb,NaPi-Ⅱb)促进断奶仔猪对磷的吸收[28],但这种调节机制有待进一步研究。研究还表明,EGF对Na+[29]、Cl-[30]、Mg2+[31]、5-羟色胺(serotonin,5-HT)[32]等营养物质吸收具有调控作用,但是否对断奶仔猪起作用,尚未见研究报道。综上所述,EGF可通过促进断奶仔猪肠上皮细胞增殖与分化、肠道绒毛发育、胃肠道消化酶的分泌、营养物质消化吸收,从而提高仔猪生长性能。
2、 EGF对断奶仔猪肠道屏障功能的影响
肠道不仅是营养物质消化吸收的主要部位,也是机体防御外界刺激的重要屏障。仔猪断奶可能会因为饮食及环境的改变而发生断奶应激,破坏仔猪肠道屏障功能,影响动物肠道健康。EGF是一种肠道营养因子,对肠道机械(物理)屏障、化学屏障、免疫屏障与微生物屏障功都具有良好的调节作用[12,18,19,33,34]。
2.1、 EGF促进紧密连接蛋白相关基因表达
肠上皮是由单层肠上皮细胞增殖与分化而来,将肠黏膜与肠腔分离开来。紧密连接是肠黏膜机械屏障中最重要的结构,主要由闭合蛋白(claudins)、闭锁蛋白(occludin)及连接黏附分子(junctional adhesion molecule,JAM)等组成,并与闭合小环蛋白(zona occludens,ZO)-1、ZO-2、ZO-3等支架蛋白相互作用形成肠道物理屏障[9]。前人研究表明,EGF可通过促进紧密连接蛋白相关基因表达,调节动物肠道屏障功能[33,34]。Geng等[34]用肠缺血再灌注损伤大鼠试验发现,注射EGF可上调肠道紧密连接蛋白ZO-1及occludin的表达。Clark等[35]以坏死性肠炎(NEC)损伤大鼠模型进行试验,结果表明EGF可通过调节肠道occludin和claudin-3的表达来缓减大鼠NEC损伤。人Caco-2细胞试验表明,EGF可增强肌动蛋白细胞骨架的稳定性,上调纤维形肌动蛋白(F-actin)表达,下调球形肌动蛋白(G-actin)表达[36,37],降低细胞通透性、酪氨酸磷酸化和苏氨酸去磷酸化作用,减弱occludin及ZO-1在细胞连接处的重新分配,维持细胞物理屏障功能[33,38,39,40]。Kaur等[41]用艰难梭菌(C.difficile)感染小鼠,发现C.difficile可导致小鼠肠道的紧密连接蛋白表达紊乱,而EGF作用后可促进肠道紧密连接表达,恢复肠道屏障功能。刘淑杰等[10]利用葡聚糖硫酸钠构建小鼠结肠炎模型,发现EGF可通过提高肠道occludin的表达修复小鼠受损的肠道组织,维持肠道黏膜屏障的完整性。
断奶应激会破坏仔猪肠道屏障功能,导致仔猪抵御病原微生物能力下降,造成营养物质消化吸收障碍,引起仔猪腹泻等肠道疾病的发生,并最终造成仔猪生长性能下降[5,6,24]。在断奶仔猪上的研究表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪肠道紧密连接蛋白相关基因表达,维持仔猪肠道屏障功能[14,22]。如Xu等[14]研究表明,仔猪摄取一定量的EGF可促进空肠紧密连接蛋白ZO-1、claudin-1和occludin mRNA的表达。汤小朋[22]研究发现,EGF对LPS刺激导致的紧密连接紊乱具有调节作用,可促进仔猪空肠及回肠ZO-1、claudin-1和occludin mRNA的表达。但是,目前关于EGF对断奶仔猪肠道物理屏障功能的作用机制研究尚不够深入,对EGF调控断奶仔猪肠道紧密连接蛋白相关基因表达的机制需进一步试验研究。
2.2、 EGF促进断奶仔猪肠道黏蛋白2(Muc2)的分泌
黏液层是保护肠道上皮细胞免受病原微生物侵害的第1道防线,对维持肠道内环境的动态平衡具有重要作用。黏蛋白(Mucs)是黏液的主要构成部分,Mucs的分泌对肠道屏障功能的维持具有重要意义。研究表明EGF对Mucs的分泌具有促进作用[19,35]。Clark等[35]研究表明,EGF可通过调节肠道Muc2的分泌来减缓大鼠NEC损伤。人Caco-2细胞试验表明,EGF可通过激活细胞外信号调节激酶1/2-蛋白激酶C(ERK1/2-PKC)信号通路,调节细胞双重氧化酶2(dual oxidases 2,DUOX2)的分泌,促进黏蛋白5AC(M uc5AC)及黏蛋白3(Muc3)的分泌来增强肠上皮细胞化学屏障功能,阻止病原体的侵袭[42]。断奶仔猪上的研究表明,EGF主要通过促进肠道Muc2的分泌来维持肠道化学屏障功能[18,22,43]。Muc2是肠道中主要的分泌型黏蛋白,主要由肠道杯状细胞分泌产生[9,44]。Bedford等[19]研究表明,EGF可促进肠道杯状细胞的分化,从而促进肠道Muc2的分泌,维持黏液的更新换代。汤小朋[22]研究表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪空肠及回肠Muc2 mRNA的表达,且对LPS导致的受损肠道的Muc2 mRNA表达也具有促进作用。Wang等[43]研究同样表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪肠道Muc2 mRNA表达。以上结果表明,EGF可通过促进肠道化学屏障功能维持断奶仔猪肠道屏障功能完整性。
2.3 、EGF增强断奶仔猪肠道免疫功能
肠黏膜免疫屏障是动物抵抗外界病原体入侵机体的重要屏障,主要由派伊氏结、黏膜淋巴集合体、弥散黏膜淋巴组织、免疫细胞、免疫球蛋白(immunoglobulin,Ig)及细胞因子(抗炎细胞因子、促炎细胞因子)组成。研究表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪免疫功能的发育,提高肠黏膜免疫屏障功能,减少病原体侵袭的发生[18,19,45]。Wang等[18]研究表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪十二指肠IgA、IgM、IgG水平。Bedford等[19]研究表明,EGF可促进断奶仔猪肠道抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素-13(interleukin 13,IL-13)的分泌。汤小朋[22]体内外研究表明,EGF可降低IPEC-J2细胞及断奶仔猪空肠及回肠促炎因子白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)mRNA表达。Lee等[45]研究表明,EGF可促进仔猪断奶后28 d空肠黏膜IgA水平。以上研究表明,EGF可通过提高断奶仔猪肠道免疫球蛋白水平,促进抗炎因子分泌,抑制促炎因子分泌来提高仔猪免疫屏障功能。
2.4 、EGF促进有益菌定植
肠道正常微生物菌群在维持肠道屏障功能中发挥着重要作用。益生菌可通过竞争性黏附肠道上皮细胞结合位点减少病原菌的黏附。EGF可促进有益菌定植,抑制有害菌定植[12,22,46]。如Wang等[12]研究表明,EGF可降低断奶仔猪回肠中有害微生物大肠杆菌(E.coli)及肠球菌的数量,增加回肠及盲肠中有益微生物乳酸菌的数量,使仔猪肠道处于一个健康状态。汤小朋[22]研究表明,EGF可抑制断奶仔猪空肠有害菌沙门氏菌的繁殖,从而维护动物肠道健康。动物肠道共生着数以亿计的微生物,与宿主协同进化,构成一个动态平衡的微生态系统,共同维护动物肠道屏障功能[47]。肠道微生物可通过自身或自身所产生的代谢物参与肠黏膜中免疫细胞的增殖和分化,从而实现对肠黏膜免疫系统的调控[48,49]。如脆弱拟杆菌可通过多聚糖A诱导调节性T细胞(Treg)发育[50],可通过促进白细胞介素-17(IL-17)的生成,进而促进辅助性T细胞的增殖[51]。EGF对肠道微生物及免疫功能均具有调节作用,但EGF是否通过微生物的调节来调控断奶仔猪肠道免疫功能,尚需进一步研究,这也是今后研究的重要方向。综上所述,EGF可通过调节断奶仔猪肠道机械(物理)屏障、化学屏障、免疫屏障与微生物屏障来维持断奶仔猪肠道健康(图1)。
图1 EGF通过促进肠道屏障功能促进断奶仔猪肠道健康
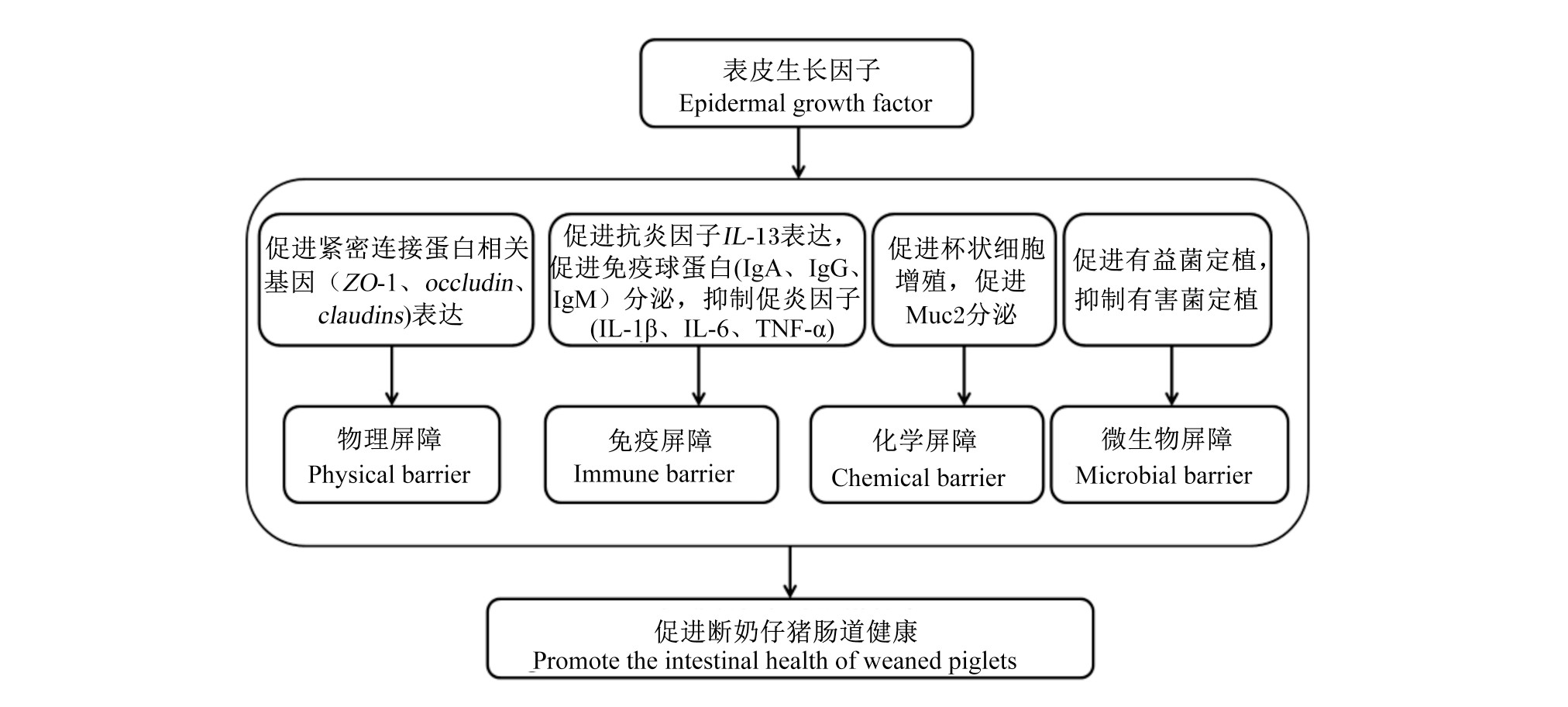
Fig.1 EGF via promoting intestinal barrier function to promote intestinal health of w eaned piglets
ZO-1:闭合小环蛋白zona occluden-1;occludin:闭锁蛋白;claudins:闭合蛋白;IL-13:白细胞介素-13 interleukin-13;IgA:免疫球蛋白A immunoglobulin A;IgG:免疫球蛋白G immunoglobulin G;IgM:免疫球蛋白M immunoglobulin M;IL-1β:白细胞介素-1βinterleukin-1β;IL-6:白细胞介素-6 interleukin-6;TNF-α:肿瘤坏死因子-αtumor necrosis factor-α;Muc2:黏蛋白2 M ucin 2。
3 、EGF对断奶仔猪肠道抗氧化功能的影响
断奶对仔猪是一种应激反应,不仅破坏肠道黏膜屏障功能[3,4],还会破坏机体氧化-抗氧化系统的动态平衡,诱导氧化应激反应[3,52]。氧化应激与动物肠道损伤密切相关[53]。机体在正常的新陈代谢过程中会不断地生成活性氧(ROS),并与机体内的抗氧化系统保持良好的动态平衡,而当机体产生的ROS水平高于机体清除能力时,就会诱发氧化应激,导致氧化损伤,诱导细胞凋亡,破坏肠道屏障功能[3,54]。断奶应激是养猪生产中普遍存在且不可避免的应激现象,对养猪生产产生不利影响。Yin等[3]研究发现,仔猪断奶后1 d,血清中蛋白质氧化损伤标志物蛋白羟基(protein carbonyl,PCO)显着含量,断奶后3 d血清中丙二醛(malonaldehyde,MDA)含量显着上升,说明断奶诱导了仔猪氧化应激的发生。肠道是响应氧化应激反应的重要器官。Cao等[55]研究发现,仔猪断奶后,空肠MDA含量显着提高,抗氧化酶谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶-1(GPX-1)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶-4(G PX-4),铜锌超氧化物歧化酶(Cu/Zn-SOD)、锰超氧化物歧化酶(Mn-SOD)基因表达显着下调,说明断奶诱导了仔猪氧化应激的发生。因此,通过营养手段缓解断奶应激造成的仔猪氧化损伤对提高仔猪生产效率具有重要意义。研究表明通过营养手段,如饲粮中添加谷氨酰胺[56]、褐藻寡糖[57]等功能性添加剂可增强仔猪机体抗氧化功能,并显着缓解断奶诱导的氧化应激反应。EGF是一种重要的细胞保护小肽,具有一定的抗氧化功能,对小肠缺血-再灌注诱导的氧化损伤具有缓解作用[58]。Tang等[7]在IPEC-J2细胞中的研究表明,LPS刺激可诱导IPEC-J2细胞氧化损伤的发生,氧化应激进一步加速了细胞凋亡,而EGF可通过激活核因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2,Nrf2)进而介导抗氧化酶基因,如超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-Px)和Ⅱ相代谢酶基因,如血红素氧化酶-1(heme oxygenase,HO-1)、醌氧化还原酶1(quinone oxidoreductase,NQO1)的表达来缓解猪小肠上皮细胞氧化损伤,并通过线粒体途径—B细胞淋巴瘤-2/半胱天冬酶-9(Bcl2/caspase 9)及死亡受体途径———死亡因子受体/半胱天冬酶8(Fas/caspase 8)来降低氧化应激诱导的IPEC-J2细胞凋亡。因此,推测EGF对断奶仔猪氧化应激也具有缓解作用,可通过缓解肠道氧化损伤,促进断奶仔猪肠道健康,但这需要试验进一步证实。
4、 小结
EGF是一种重要的肠道调节剂,对维持动物肠道健康有着至关重要的作用。EGF对断奶仔猪肠道健康具有良好的调节作用,其调控仔猪肠道健康的可能机制为:1)通过调节仔猪肠道发育,促进肠道消化酶活性分泌及营养物质转运载体的表达,促进仔猪营养物质消化吸收率,降低腹泻率,提高生长性能。2)通过提高断奶仔猪肠道屏障功能(促进紧密连接蛋白表达,促进黏蛋白分泌,促进免疫球蛋白及抗炎细胞因子分泌,减少促炎细胞因子分泌,提高有益菌的定植,减少有害微生物定植),维持断奶仔猪肠道完整性。3)还可能通过缓解肠道氧化损伤,进而改善仔猪肠道健康状况。
参考文献
[1] WHITING T L,PASMA T.Isolated weaning technology:humane benefits and concerns in the production of pork[J].The Canadian V eterinary Journal,2008,49(3):293-301.
[2] LODEMANN U,AMASHEH S,RADLOFF J,et al.Effects of ex vivo infection with ETEC on jejunal barrier properties and cytokine expression in pro bio ticsupplemented pigs[J].Digestive Diseases and Sciences,2017,62(4):922-933.
[3] YIN J,WU M M,XIAO H,et al.Development of an antioxidant system after early weaning in piglets[J].Journal of Animal Science,2014,92(2):612-619.
[4] EL-ZAATARI M,KAO J Y.Role of dietary metabolites in regulating the host immune response in gastrointestinal disease[J].Frontiers in Immunology,2017,8:51.
[5] XIAO K,JIAO L F,CAO S T,et al.Whey protein concentrate enhances intestinal integrity and influencestransform ing growth factor-β1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways in piglets after lipopolysaccharide challenge[J].B ritish Journal of N utrition,2016,115(6):984-993.
[6] HEO J M,OPAPEJU F O,PLUSKE J R,et al.Gastrointestinal health and function in weaned pigs:a review of feeding strategies to control post-weaning diarrhoea without using in-feed antimicrobial compounds[J].Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition,2013,97(2):207-237.
[7] TANG X P,LIU B,WANG X R,et al.Epidermal growth factor,through alleviating oxidative stress,protect IPEC-J2 cells from lipo polysaccharides-induced apoptosis[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2018,19(3):848.
[8] TANG X P,FANG R J,PAN G C,et al.Acute effect of epidermal growth factor on phosphate diffusion across intestinal mucosa of hens using the Ussing chamber system[J].Pakistan Journal of Zoology,2019,51(6):2209-2216.
[9] TANG X P,LIU H,YANG S F,et al.Epidermal growth factor and intestinal barrier function[J].Mediators of Inflammation,2016,2016:1927348.
[10] 刘淑杰,邓波,徐子伟.表皮生长因子对葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的结肠炎模型小鼠肠道损伤的修复研究[J].动物营养学报,2016,28(6):1735-1741.LIU S,DENG B,XU Z.Study on intestinal damage repair of epidermal growth factor on dextra sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2016,28(6):1735-1741.(in Chinese)
[11] SHEN W H,XU R J.Stability and distribution of orally administered epidermal growth factor in neonatal pigs[J].Life Sciences,1998,63(10):809-820.
[12] WANG D Y,XU S Y,LIN Y,et al.Recombinant porcine epidermal growth factor-secreting Lactococcus lactis promotes the growth performance of earlyweaned piglets[J].BMC Veterinary Research,2014,10:171.
[13] 朱繁,王丽霞,贾杏林,等.饲粮中添加表皮生长因子对断奶仔猪血清生化指标、血清游离氨基酸和小肠黏膜水解氨基酸含量的影响[J].动物营养学报,2018,30(7):2519-2528.ZHU F,WANG L,JIA X,et al.Effects of dietary epidermal growth factor on serum biochemical indices,serum free amino acid and intestinal mucosal hydrolytic amino acid contents of weaned piglets[J].ChineseJournal of Animal Nutrition,2018,30(7):2519-2528.(in Chinese)
[14] XU S,WAN G D,ZHANG P,et al.Oral administration of Lactococcus lactis-expressed recombinant porcine epidermal growth factor stimulates the development and promotes the health of small intestines in earlyweaned piglets[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2015,119(1):225-235.
[15] CHEUNG Q C K,YUAN Z F,DYCE P W,et al.Generation of epidermal growth factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis and its enhancement on intestinal development and growth of early-weaned mice[J].The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,2009,89(3):871-879.
[16] KANG P,TOMS D,YIN Y L,et al.Epiderm al growth factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis enhances intestinal development of early-weaned pigs[J].The Journal of Nutrition,2010,140(4):806-811.
[17] WANG S J,GUO C H,ZHOU L,et al.Comparison of the biological activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae-expressed intracellular EGF,extracellular EGF,and tagged EGF in early-weaned pigs[J].Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2015,99(17):7125-7135.
[18] WANG S J,GUO C H,ZHOU L,et al.Effects of dietary supplementation with epidermal growth factor-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae on duodenal development in weaned piglets[J].B ritish Journal of Nutrition,2016,115(9):1509-1520.
[19] BEDFORD A,CHEN T,HUYNH E,et al.Epidermal growth factor containing culture supernatant enhances intestine development of early-weaned pigs in vivo:potential mechanisms[J].Journal of Biotechnology,2015,196/197:9-19.
[20] WANG L X,ZHU F S,YANG H Z,et al.Effects of dietary supplementation with epidermal growth factor on nutrient digestibility,intestinal development and expression of nutrient transporters in early-weaned piglets[J].Journal of Animal Physiology&Animal Nutrition,2019,103(2):618-625.
[21] WANG L X,ZHU F,YANG H S,et al.Epidermal growth factor improves intestinal morphology by stimulating proliferation and differentiation of enterocytes and mTOR signaling pathway in weaning piglets[J].Science China Life Sciences,2020,63(2):259-268.
[22] 汤小朋.表皮生长因子对脂多糖诱导的仔猪肠道屏障功能及磷吸收影响研究[D].博士学位论文.长沙:湖南农业大学,2018.TANG X.The study of influences of epidermal growth factor on intestinal barrier function and phosphorus absorption of weaned piglets[D].Ph.D.Thesis.Changsha:Hunan Agricultural U niversity,2018.(in Chinese)
[23] LEE D N,CHUANG Y S,CHIOU H Y,et al.Oral administration recombinant porcine epidermal growth factor enhances the jejunal digestive enzyme genes expression and activity of early-weaned piglets[J].Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition,2008,92(4):463-470.
[24] BEDFORD A,HU YNH E,FU M L,et al.Growth performance of early-weaned pigs is enhanced by feeding epiderm al growth factor-expressing Lac tococcus lactis fermentation product[J].Journal of Biotechnology,2014,173:47-52.
[25] TANG X P,XIONG K N.Effects of epidermal growth factor on glutamine and glucose absorption by IPECJ2 cells challenged by lipopoly saccharide using the Ussing chamber system[J].Pakistan Journal of Zoology,2020,doi:10.17582/journal.pjz/20200117080156.
[26] XU H,MICHAEL I,ERIC R,et al.Transcriptional regulation of the human NaPi-Ⅱb cotransporter by EGF in Caco-2 cells involves c-myb[J].American Journal of Physio logy-Cell Physiology,2003,284:C1262-C1271.
[27] XING T,TAN X,Y U Q,et al.Identifying the location of epidermal growth factor-responsive element involved in the regulation of typeⅡb sodium-phosphate cotransporter expression in porcine intestinal epithelial cells[J].Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal N utrition,2017,101(6):1249-1258.
[28] 汤小朋,徐荣,李成良,等.表皮生长因子对脂多糖刺激断奶仔猪肠道钠磷转运载体蛋白Ⅱb表达的影响[J].动物营养学报,2018,30(10):4020-4027.TANG X,XU R,LI C,et al.Effects of epidermal growth factor on intestinal typeⅡb sodium-phosphate cotransporter expression of weaned piglets challenged by lipopolysaccharide[J].Chinese Journal of Animal N utrition,2018,30(10):4020-4027.(in C hinese)
[29] ZHELEZNOVA N N,WILSON P D,STARUSCHENKO A.Epidermal growth factor-mediated proliferation and sodium transport in normal and PKD epithelial cells[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta:Molecular Basis of Disease,2011,1812(10):1301-1313.
[30] O’MAHONY F,TO U MI F,MROZ M S,et al.Induc-tion of Na~+/K~+/2Cl~-cotransporter expression mediates chronic potentiation of intestinal epithelial Cl~-secretion by EGF[J].American Journal of PhysiologyC ell Physiology,2008,294(6):C1362-C1370.
[31] BEZZERIDES V J,RAMSEY I S,KOTECHA S,et al.Rapid vesicular translocation and insertion of TRP channels[J].Nature Cell Biology,2004,6(8):709-720.
[32] GILL R K,ANBAZHAGAN A N,ESMAILI A,et al.Epidermal growth factor upregulates serotonin transporter in human intestinal epithelial cells via transcriptional mechanisms[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2011,300(4):G627-G636.
[33] SUZUKI T,SETH A,RAO R.Role of phospholipase Cγ-induced activation of protein kinase Cε(PKCε)and PKCβI in epidermal growth factor-mediated protection of tight junctions from acetaldehyde in Caco-2cell monolayers[J].The Journal of Biological C hemistry,2008,283(6):3574-3583.
[34] GENG Y X,LI J S,WANG F,et al.Epiderm al growth factor promotes proliferation and imprves restoration after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats[J].Inflammation,2013,36(3):670-679.
[35] CLARK J A,DOELL S M,HALPERN M D,et al.Intestinal barrier failure during experimental necrotizing enterocolitis:protective effect of EGF treatment[J].Am eric an Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiolo gy,2006,291:G938-G949.
[36] BANAN A,ZHANG L J,FARHADI A,et al.PKC-β1isoform activation is required for EGF-induced NF-κB inactivation and IκBαstabilization and protection of Factin assembly and barrier function in enterocyte monolayers[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2004,286(3):C723-C738.
[37] BANAN A,ZHANG L J,SHAIKH M,et al.Inhibition of oxidant-induced nuclear factor-κB activation and inhibitory-κBαdegradation and instability of F-actin cytoskeletal dynamics and barrier function by epidermal growth factor:key role of phospholipase-γisoform[J].Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics,2004,309(1):356-368.
[38] BASUROY S,SETH A,ELIAS B,et al.MAPK interacts with occludin and mediates EGF-induced prevention of tight junction disruption by hydrogen peroxide[J].Biochemical Journal,2006,393(1):69-77.
[39] SHETH P,SETH A,THANGAVEL M,et al.Epidermal growth factor prevents acetaldehyde-induced para-cellular permeability in Caco-2 cell monolayer[J].Alcoholism:Clinical and Experimental Research,2004,28(5):797-804.
[40] SAMAK G,AGGARWAL S,RAO R K.ERK is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions,but not adherens junctions,in acetaldehyde-treated Caco-2 cell monolayers[J].American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2011,301(1):G50-G59.
[41] DAMIANO S,MORANO A,UCCI V,et al.Dual oxidase 2 generated reactive oxygen species selectively mediate the induction of mucins by epidermal growth factor in enterocytes[J].The International Journal of Biochemistry&Cell Biology,2015,60:8-18.
[42] KAUR S,VAISHNAVI C,RAY P,et al.Preliminary investigation on the effect of Lactobacillus and epidermal growth factor on tight junction proteins in experimental clostridium difficile infection[J].Advances in Microbiology,2014,4(8):425-435.
[43] WANG L X,ZHU F,LI J Z,et al.Epidermal growth factor promotes intestinal secretory cell differentiation in weaning piglets via Wnt/β-catenin signalling[J].Animal,2020,14(4):790-798.
[44] 汤小朋,熊康宁.表皮生长因子对动物肠道黏蛋白分泌的影响及其作用机制[J].生命科学研究,2020,24(2):168-172.TANG X,XIONG K.Effects of epidermal growth factor on intestinal mucin secretion and its action mechanism[J].Life Science Research,2020,24(2):168-172.(in C hinese)
[45] LEE D N,KUO T Y,CHEN M C,et al.Expression of porcine epidermal growth factor in Pichia pastoris and its biology activity in early-weaned piglets[J].Life Sciences,2006,78(6):649-654.
[46] ZHANG Z W,CAO L L,ZHOU Y,et al.Analysis of the duodenal microbiotas of weaned piglet fed with epidermal growth factor-expressed Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J].BMC Microbiology,2016,16:166.
[47] 朱丽慧,廖荣荣,杨长锁.肠道微生物对家禽肠道免疫功能的调节作用及其机制[J].动物营养学报,2018,30(3):820-828.ZHU L,LIAO R,YANG C.Immunity system regulated by gut microbiota of poultry and its mechanisms[J].Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2018,30(3):820-828.(in Chinese)
[48] WESEMANN D R,PORTUGUESE A J,MEYERS R M,et al.Microbial colonization influences early B-lin-eage development in the gut lamina propria[J].Nature,2013,501(7465):112-115.
[49] SUN M,HE C,CONG Y,et al.Regulatory immune cells in regulation of intestinal inflammatory response to microbiota[J].M ucosal Immunology,2015,8(5):969-978.
[50] LEV Y M,KOLODZIEJCZYK A A,THAISS C A,et al.Dysbiosis and the immune system[J].Nature Reviews Immunology,2017,17(4):219-232.
[51] HORAI R,SEN H N,CASPI R R.Commensal microbiota as a potential trigger of autoimmune uveitis[J].Expert Review of Clinical Imm unology,2017,13(4):291-293.
[52] LUO Z,ZHU W,GUO Q,et al.Weaning induced hepatic oxidative stress,apoptosis,and aminotransferases through MAPK signaling pathways in piglets[J].Oxidative M edicine and Cellular Longevity,2016,2016:4768541.
[53] 王斐,何进田,沈明明,等.姜黄素对宫内发育迟缓断奶仔猪肠道抗氧化功能的影响[J].食品科学,2019,40(15):177-183.WANG F,HE J,SHEN M,et al.Effect of curcumin supplementation on intestinal antioxidant function in weaning piglets with intrauterine growth retardation[J].Food Science,2019,40(15):177-183.(in Chinese)
[54] HUANG C X,LV B,WANG Y.Protein phosphatase2A mediates oxidative stress induced apoptosis in osteoblasts[J].Mediators of Inflammation,2015,2015:804260.
[55] CAO S T,WANG C C,WU H,et al.Weaning disrupts intestinal antioxidant status,impairs intestinal barrier and mitochondrial function,and triggers mitophagy in piglets[J].Journal of Animal Science,2018,96(3):1073-1083.
[56] WANG J J,CHEN L X,LI P,et al.Gene expression is altered in piglet small intestine by weaning and dietary glutamine supplementation[J].The Journal of Nutrition,2008,138(6):1025-1032.
[57] WAN J,ZHANG J,CHEN D W,et al.Alginate oligosaccharide enhances intestinal integrity of weaned pigs through altering intestinal inflammatory responses and antioxidant status[J].RSC Advances,2018,8(24):13482-13492.
[58] ARDA-PIRINCCI P,BOLKENT S.The role of epidermal growth factor in prevention of oxidative injury and apoptosis induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats[J].Acta Histochemica,2014,116(1):167-175.





