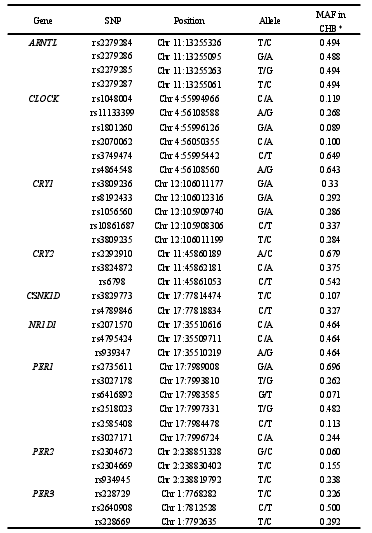
本研究共挑选生物钟通路相关基因功能性 SNP 位点 55 个,除 rs2279286、rs939347 外、其余 SNPs 检出率均超过 95%。经哈迪温伯格平衡检验,7 个 SNP(rs11133399, rs3809235, rs3824872, rs939347, rs11588258, rs12045886, rs3027171)不符合哈迪温伯格平衡,如表 4 所示,有 48 个 SNP 位点被纳入后续的研究,其中有 5 个位于 ARNTL 上,4 个位于 CLOCK 上,4 个位于 CRY1 上,2 个位于CRY2 上,2 个位于 CSNK1D 上,2 个位于 NR1D1 上,5 个位于 PER1 上,3 个位于 PER2 上,3 个位于 PER3 上,3 个位于 RORA 上,6 个位于 RORB 上,9个位于 RORC 上。另外发现,RORB 上的 rs2273975、rs4376556 和 rs7846903位点的三种基因型在病例组和对照组中的分布差异有统计学意义(P=0.027、P=0.021、P=0.022)。
参考文献
[1] Forouzanfar M H, Liu P, Roth G A, et al. Global Burden of Hypertension and SystolicBlood Pressure of at Least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990-2015[J]. JAMA,2017,317(2):165-182.
[2] World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014[R].Geneva, World Health Organization,2014.
[3] Kearney P M, Whelton M, Reynolds K, et al. Global burden of hypertension: analysis ofworldwide data.[J]. Lancet,2005,365(9455):217-223.
[4] Wang Z, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al. Status of Hypertension in China: Results From the ChinaHypertension Survey, 2012-2015[J]. Circulation, 2018,137(22):2344-2356.
[5] Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195countries and territories, 1980-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of DiseaseStudy 2017[J]. Lancet, 2018,392(10159):1736-1788.
[6] Bundy J D, He J. Hypertension and Related Cardiovascular Disease Burden in China[J].Ann Glob Health, 2016,82(2):227-233.
[7] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会.中国高血压防治指南(2018 年修订版)[J].中华心血管病杂志,2019,24(01):24-56.
[8] Richards J, Gumz M L. Mechanism of the circadian clock in physiology[J]. AMERICANJOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY-REGULATORY INTEGRATIVE AND COMPARATIVEPHYSIOLOGY, 2013,304(12):R1053-R1064.
[9] Degaute J, van de Borne P, Linkowski P, et al. Quantitative Analysis of the 24-Hour BloodPressure and Heart Rate Patterns in Young Men[J]. Hypertension, 1991,18(2):199-210.
[10] Douma L G, Gumz M L. Circadian clock-mediated regulation of blood pressure[J]. FreeRadic Biol Med, 2018,119:108-114.
[11] Partch C L, Green C B, Takahashi J S. Molecular architecture of the mammalian circadianclock.[J]. Trends Cell Biol,2014,24(2):90-99.
[12] Dunlap J C. Molecular bases for circadian clocks.[J]. Cell,1999,96(2):271-290.
[13] Bunger M K, Wilsbacher L D, Moran S M, et al. Mop3 is an essential component of themaster circadian pacemaker in mammals.[J]. Cell,2000,103(7):1009-1017.
[14] Kimura Y, Honda M, Sasaki R, et al. The circadian rhythm of bladder clock genes in thespontaneously hypersensitive rat[J]. PLoS One, 2019,14(7):e220381.
[15] Xie Z, Su W, Liu S, et al. Smooth-muscle BMAL1 participates in blood pressure circadianrhythm regulation.[J]. J Clin Invest,2015,125(1):324-336.
[16] Nakashima A, Kawamoto T, Noshiro M, et al. Dec1 and CLOCK Regulate Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase beta1 Subunit Expression and Blood Pressure[J]. Hypertension, 2018,72(3):746-7[17] Leu H B, Chung C M, Lin S J, et al. Association of circadian genes with diurnal bloodpressure changes and non-dipper essential hypertension: a genetic association withyoung-onset hypertension.[J]. Hypertens Res,2015,38(2):155-162.
[18] Ramirez-Bello J, Jimenez-Morales M. [Functional implications of single nucleotidepolymorphisms (SNPs) in protein-coding and non-coding RNA genes in multifactorialdiseases][J]. Gac Med Mex, 2017,153(2):238-250.
[19] Yang J, Benyamin B, McEvoy B P, et al. Common SNPs explain a large proportion of theheritability for human height[J]. Nature Genetics, 2010,42(7):565-569.
[20] 王瑞恒, 刘利民, 赵金玲.我国 3 个民族 13 个 SNPs 位点多态性及遗传学关系的比较[J].遗传,2009(03):273-279.
[21] Hindorff L A, Sethupathy P, Junkins H A, et al. Potential etiologic and functionalimplications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits[J]. Proceedings of theNational Academy of Sciences,2009,106(23):9362-9367.
[22] 娄娇. 基于表达数量性状位点(eQTL)定位分析策略的结直肠癌遗传易感性研究[D].华中科技大学, 2016.
[23] 苑芳芬. 钾离子通道及其互作蛋白基因遗传变异与注意缺陷多动障碍的关联研究[D].华中科技大学, 2017.
[24] Xu Y, Ma P, Shah P, et al. Non-optimal codon usage is a mechanism to achieve circadianclock conditionality[J]. Nature, 2013,495(7439):116-120.
[25] Bass J, Takahashi J S. Circadian integration of metabolism and energetics[J]. Science,2010,330(6009):1349-1354.
[26] Yang G, Paschos G, Curtis A M, et al. Knitting up the raveled sleave of care[J]. Sci TranslMed, 2013,5(212):212r-213r.
[27] Reilly D F, Westgate E J, FitzGerald G A. Peripheral circadian clocks in the vasculature[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2007,27(8):1694-1705.
[28] Curtis A M, Cheng Y, Kapoor S, et al. Circadian Variation of Blood Pressure and theVascular Response to Asynchronous Stress[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy ofSciences of the United States of America, 2007,104(9):3450-3455.
[29] Zuber A M, Centeno G, Pradervand S, et al. Molecular clock is involved in predictivecircadian adjustment of renal function[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2009,106(38):16523-16528.
[30] Solocinski K, Holzworth M, Wen X, et al. HHS Public Access[J]. Acta Physiol (Oxf),2017,220(1):72-82.
[31] Vukolic A, Antic V, Van Vliet B N, et al. Role of mutation of the circadian clock gene Per2in cardiovascular circadian rhythms[J]. American journal of physiology. Regulatory,integrative and comparative physiology, 2010,298(3):R627-R634.
[32] Stow L R, Richards J, Cheng K, et al. The Circadian Protein Period 1 Contributes to BloodPressure Control and Coordinately Regulates Renal Sodium Transport Genes[J].
Hypertension, 2012,59(6):1151-1156.
[33] Masuki S, Todo T, Nakano Y, et al. Reduced alpha-adrenoceptor responsiveness andenhanced baroreflex sensitivity in Cry-deficient mice lacking a biological clock[J]. JPhysiol, 2005,566(Pt 1):213-224.
[34] Doi M, Takahashi Y, Komatsu R, et al. Salt-sensitive hypertension in circadianclock-deficient Cry-null mice involves dysregulated adrenal Hsd3b6[J]. Nature medicine,2010,16(1):67-74.
[35] Chen L, Yang G. Recent advances in circadian rhythms in cardiovascular system[J].Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2015,6:71.
[36] Astiz M, Heyde I, Oster H. Mechanisms of Communication in the Mammalian CircadianTiming System[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019,20(2):343.
[37] Manosroi W, Williams G H. Genetics of Human Primary Hypertension: Focus on HormonalMechanisms[J]. Endocr Rev, 2019,40(3):825-856.
[38] 王亚萍. 基因多态性的研究方法及其临床应用[J]. 临床医学, 2003(09):49-50.
[39] 张桂荣, 张玲. 基因多态性检测分析方法与疾病诊断[J]. 吉林医学, 2001(06):325-327.
[40] B?nnelykke K, Sparks R, Waage J, et al. Genetics of allergy and allergic sensitization:common variants, rare mutations[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2015,36:115-126.
[41] Zeng P, Zhao Y, Qian C, et al. Statistical analysis for genome-wide association study[J].Journal of Biomedical Research, 2015,29(4):285-297.
[42] Kato N. Insights into the genetic basis of type 2 diabetes[J]. Journal of DiabetesInvestigation, 2013,4(3):233-244.
[43] Corella D, Asensio E M, Coltell O, et al. CLOCK gene variation is associated withincidence of type-2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in type-2 diabetic subjects: dietarymodulation in the PREDIMED randomized trial[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2016,15:4.
[44] Ramírez-Bello J, Vargas-Alarcón G, Tovilla-Zárate C, et al. Polimorfismos de un solonucleótido (SNP): implicaciones funcionales de los SNP reguladores (rSNP) y de losSNP-ARN estructurales (srSNP) en enfermedades complejas[J]. Gaceta Médica de México,2013,149:220-228.
[45] Mekinian A, Tamouza R, Pavy S, et al. Functional study of TNF-alpha promoterpolymorphisms: literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Cytokine Netw,2011,22(2):88-102.
[46] Gianchecchi E, Palombi M, Fierabracci A. The putative role of the C1858T polymorphismof protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 gene in autoimmunity[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews,2013,12(7):717-725.
[47] Lin E, Kuo P, Liu Y, et al. Effects of circadian clock genes and health-related behavior onmetabolic syndrome in a Taiwanese population: Evidence from association and interactionanalysis[J]. PLOS ONE, 2017,12(3):e173861.
[48] Alli A, Yu L, Holzworth M, et al. Direct and indirect inhibition of the circadian clockprotein Per1: effects on ENaC and blood pressure[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol,2019,316(5):F807-F813.
[49] Hou T, Su W, Guo Z, et al. A Novel Diabetic Mouse Model for Real-Time Monitoring ofClock Gene Oscillation and Blood Pressure Circadian Rhythm[J]. Journal of BiologicalRhythms, 2018,34(1):51-68.
[50] Manosroi W, Williams G H. Genetics of Human Primary Hypertension: Focus on HormonalMechanisms[J]. Endocrine Reviews, 2019,40(3):825-856.